The 25 leading strategic consulting firms often use analytical models to detail time-limited collection

Including: McKinsey 7S model, Boston matrix, strategic implementation model, SWOT analysis model and so on
Background reply 1008 Free for a limited time

Consulting industry is the goal of many small partners, McKinsey, Boston, Bain and other top strategic consulting is the existence of all the industry's top, consultants how to solve problems, for enterprises to do strategic planning, consulting firms often use analytical models.
Executives at almost every large fast-forward company have been more or less trained or co- working with consulting firms, and the consulting firm's common business analysis models tend to be efficient.
Ansoff Matrix
Benchmarking
Boston Matrix (BCG Matrix)
Michael Porter's Value Chain Model
Michael Porter's Five Forces Model
Grand Strategy Matrix
Quantitative Strategic Plan Matrix
Competitive Situation Matrix (CPM Matrix)
Radar map analysis
Stakeholder Analysis
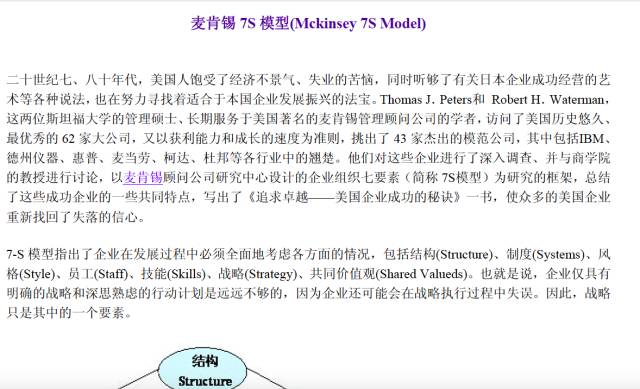
McKinsey 7S Model
McKinsey's seven-step analysis
McKinsey Consulting - A complete analysis model of marketing strategy
Internal-External Matrix (Internal-External Matrix, IE Matrix)
External Factor Evaluation Matrix (EFE Matrix)
Fish bone map analysis
Strategic Position and Action Evaluation Matrix (SPACE Matrix)
Strategy Implementation Model
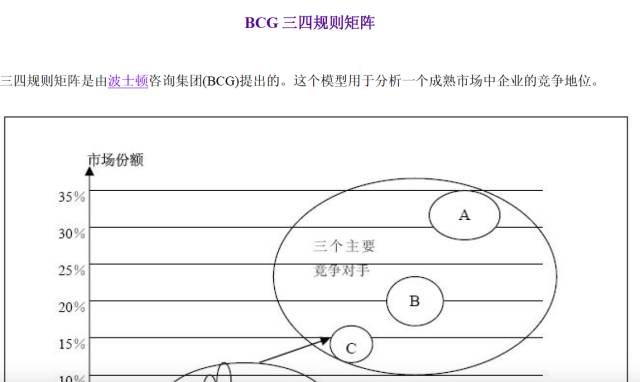
BCG three-four rule matrix
McKinsey and GE Matrix
PDCA循环(PDCA Cycle)
PEST analysis model
ROS-RMS matrix
SCP分析模型(Structure-Conduct-Performance Model)
SWOT Analysis Model (SWOT Analytics)
Here are a few brief lists, and other information on the analytical model can be viewed on its own according to the end-of-text guidelines.
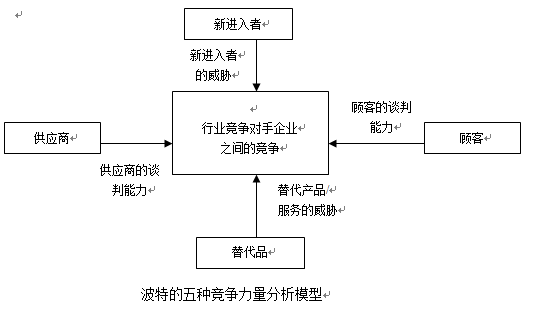
Porter's five competitiveness analysis models are widely used in strategy development in many industries. Porter argues that in any industry, domestic or international, whether it is the provision of products or services, the rules of competition are included in five competitive forces. These five competitivenesses are inter-enterprise competition, the entry of potential new competitors, the development of potential alternatives, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the bargaining power of buyers. These five competitive forces determine the profitability and level of the enterprise.
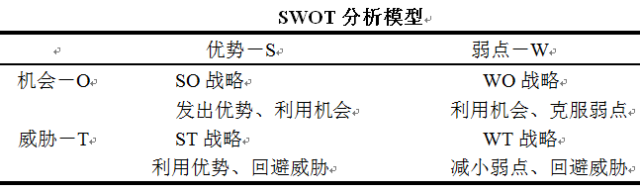
"SWOT" is an acronym for the four English words Strength, Weak, Opportunity, and Threat, a model that summarizes internal and external research findings by analyzing strengths and weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges that exist both within and outside the enterprise.
S-Advantage: Comparative analysis of the advantages of enterprises over other competitors in external market environment and internal operations;
W-disadvantage: comparative analysis of the enterprise's external market environment, internal management relative to other competitors' disadvantages;
O-Opportunity: Analysis of the development opportunities existing in enterprises under the current market competition situation;
T-Challenge: Analyze the threats and challenges existing in the current market competition.
The Strategic Position and Action Evaluation Matrix (SPACE Matrix) is primarily an analysis of the external environment of the enterprise and the strategic mix that the enterprise should adopt.
The SPACE matrix has four quadrants that represent the four strategic models of aggressiveness, conservatism, defense, and competition adopted by an enterprise. The two axles of this matrix represent two internal factors of the enterprise, financial advantage (FS) and competitive advantage (CA), and two external factors, environmental stability (ES) and industrial advantage (IS). These four factors are the most important to the overall strategic position of the enterprise.
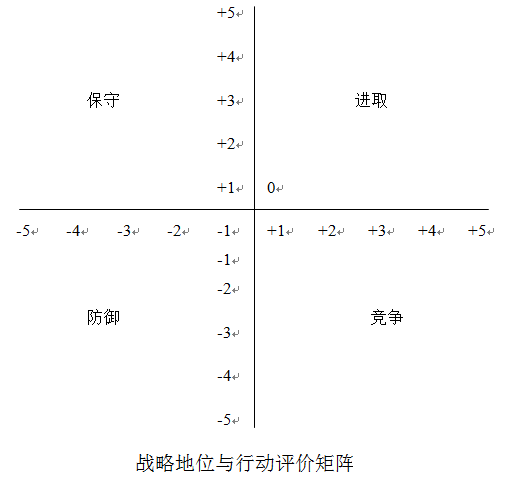
Structure, conduct, performance model to analyze possible strategic adjustments and behavioral changes when an industry or business receives a surface shock.
The SCP model analyzes the impact of external shocks from three perspectives: industry structure, business behavior and business results.

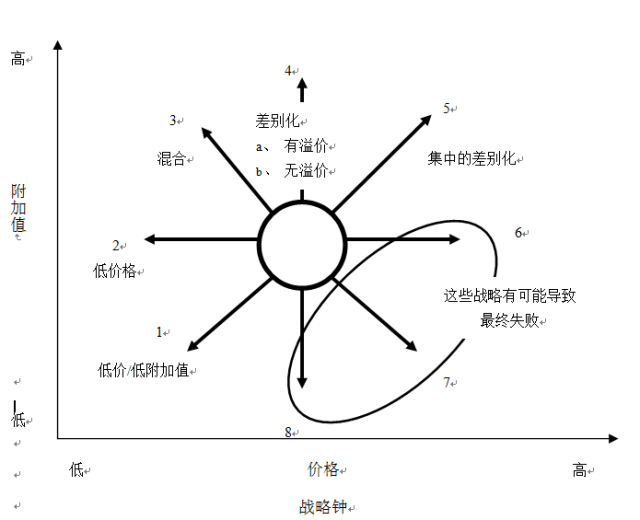
The "strategy clock" is a tool for analyzing the competitive strategy choice of the enterprise, which provides the managers and consultants of the enterprise with a way to think about the competitive strategy and gain the competitive advantage.
"The strategic clock model assumes that the suitability of products or services in different enterprises is similar, so customers may choose one of them over the other when they buy for the following reasons:
1) The price of the goods and services of this enterprise is lower than that of other companies;
2) Customers think that the company's products and services have a higher added value.
The Boston Matrix was proposed by the Boston Company, a model that is primarily used to assist companies in their business portfolios or portfolios.
The two variables in the matrix axes are the degree of growth and market share in the market in which the business unit is located. "The firm in each quadrant is in a fundamentally different cash flow position and is managed in a different way, which leads to how the firm seeks its overall business mix."
Taurus:Businesses with relatively high market share in low-growth markets generate healthy cash flow that can be used to finance other areas and grow their businesses.
Skinny Dogs:Businesses with relatively low market share are often users of medium cash flow in low-growth markets. Because of their weak competitive position, they will become a cash trap.
Star:Having a relatively high market share in a high-growth market usually requires a lot of cash to sustain growth, but having a strong market position and generating higher reported profits may be in cash balance.
Problem:Businesses with relatively low market share in fast-growing markets require significant cash inflows to finance growth.
This model is the three-three matrix used by GM and McKinsey. The two axes of this matrix represent market attractiveness and the strength or competitive position of the business unit, respectively. Where a particular business unit is in the matrix is determined by analyzing that particular business unit and industry. By versing these two variables, the business unit is determined to be located in the matrix, and thus the strategy adopted for the business unit is determined.
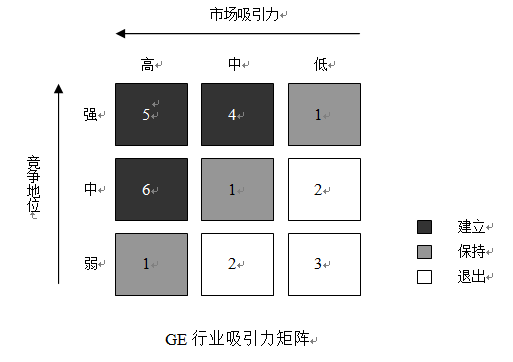
The main factors to consider for market attractiveness are:
Industry:Absolute market size, growth rate, price sensitivity, barriers to entry, alternatives, market competition, suppliers, etc.
Environment:Government regulations, economic climate, currency risk, social trends, technology, employment, interest rates, etc.
For the strength or competitive position of the business unit, the main factors to consider are:
Current benefits:Market share, market share trends, profitability, cash flow, differentiation, relative price status, etc.
Persistence:Cost, logistics, marketing, service, customer image, technology, etc.
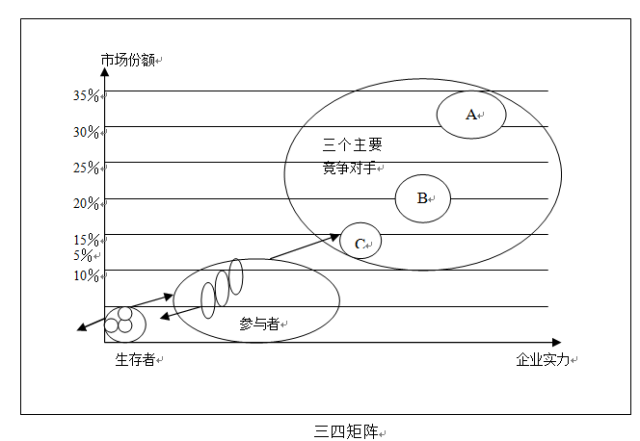
The March 4 matrix was proposed by the Boston Consulting Group. This model is used to analyze the competitive position of enterprises in a mature market.
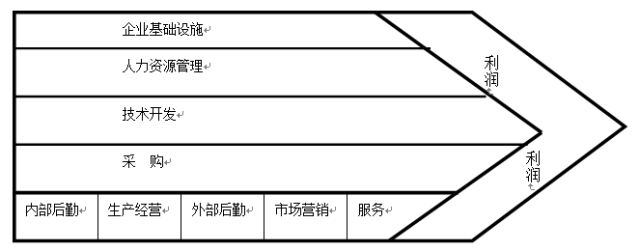
The value chain model was first proposed by Porter. Porter believes that the competitive advantage of enterprises comes from many separate activities carried out in the design, production, marketing, delivery and auxiliary processes.
There are five types of basic activities for designing competition in any industry:
Internal logistics:Activities associated with receiving, storing, and distributing, such as raw material handling, warehousing, inventory control, vehicle scheduling, and returning to suppliers.
Production jobs:Activities related to converting inputs into final product forms, such as machining, packaging, assembly, equipment maintenance, testing, etc.
External logistics:Activities related to centralizing, storing, and sending products to buyers, such as finished goods inventory management, raw material handling, delivery vehicle scheduling, etc.
Marketing and marketing:Activities related to providing buyers with ways to purchase products and guiding them to purchases, such as advertising, promotions, sales force, channel building, etc.
Service:Activities related to providing services to increase or maintain the value of the product, such as installation, repair, training, parts supply, etc.
Details of other analytical models can be viewed on their own according to the end-of-text guidelines.
How to get information
Follow"School of Evidence and Economics”
On the subscription number dialog box
Reply to keywords【1008】
Get information about how to collect it
Top strategic consulting firms often use analytical models to explain them in detail
Selected.
25 top consulting firms
Common analysis models (detailed)


How to get information
Follow"School of Evidence and Economics”
On the subscription number dialog box
Reply to keywords【1008】
Get information about how to collect it
- END -
Go to "Discovery" - "Take a look" browse "Friends are watching"