Angels, A-rounds, B-rounds, VCs, PE... Valuation methods are complete (organized version, worth reading!) )
Guide: Exactly when and what valuation method should be used has been a matter of debate in the industry. This paper hopes to find the internal relationship of various valuation methods and make some constructive suggestions. Let's start with a look at the financing history of a virtual social enterprise.
Angel Wheel: The company was founded by a serial entrepreneur and was founded with angel investment.
A round: 1 year after the company won the A round, at this time the company MAU (monthly live) reached 500,000 people, ARPU (single user contribution) for 0 yuan, revenue of 0.
A-wheel: A round after the company's rapid development of users, six months later the company obtained the A-plus round, at this time the company MAU reached 5 million people, ARPU for 1 yuan. The company began to have a certain amount of revenue (5 million yuan) because it began to get a small amount of traffic through advertising.
B round: 1 year later the company again won the B round, at this time the company MAU has reached 15 million people, ARPU for 5 yuan, the company's income has reached 75 million yuan. ARPU continues to improve because the company has found effective ways to cash in advertising, gaming, and so on.
C round: 1 year later the company obtained C round of financing, at this time the company MAU for 30 million people, ARPU for 10 yuan, the company in advertising, games, e-commerce, membership and other ways of cashing more flowering. At this time, the company's revenue reached 300 million yuan, and the company has begun to make a profit, assuming a net interest rate of 20%, 60 million.
IPO: After that, the company maintained a steady growth of 30-50% in revenue and profits each year, and went public one year after round C.
This is a typical excellent Internet enterprise financing process, founded by a continuous entrepreneur, each round has been well-known VC investment, set up about five years to list. From this company, we can see the shadow of strangers and other Internet companies. How is the company's valuation calculated in each round?
Let's make some more assumptions, in chronological order:
After the IPO, the public capital markets gave the company a price-to-earnings ratio of 50 times. Careful and professional readers will immediately react that the company's stock investment value is not very small, PEG1 (price-earnings ratio / growth), it seems that the best investment time is in the private equity stage, the money is VC and PE earned.
C round, different investment institutions gave the company different valuations, some 50 times P/E, some 10 times P/S, some a single month live valuation of 100 yuan, but the final valuation is 3 billion. Don't believe you can count. Each valuation method is logical: a company that wants to go to the GEM gives a price-to-earnings ratio of 50 times, no problem; a typical Internet company gives 10 times the market rate, which is very popular in the United States, right? Or a user's estimate of $15-20, look at the valuations of several companies, such as Facebook and Twitter, and discount them a little.
In round B, different investment institutions gave different valuation methods, and differences began to develop: an institution would only be valued at P/E, he would give the company a price-to-earnings ratio of 50 times, but the company had no profit, so the company was valued at 0; The company is valued at 10.075 billion x 750 million yuan, and an institution is valued at 100 yuan per MAU at P/MAU, so the company is valued at 100 yuan x 15 million people x 1.5 billion yuan. Different valuation methods, the difference is so big! It seems that at this point the P/E valuation method has lapsed, but P/S, P/MAU continues to apply, but the estimated price has doubled! Suppose the company ends up choosing a median of $1 billion between $750 million and $150 million and accepting an investment from VC.
Round A, P/E, P/S are invalid, but if you continue to value each user at 100 yuan, the company can also have 100 yuan / person x 5 million people x 500 million valuation. At this time can understand the company's VC is relatively small, most VC concerns are many, but the company chose a high level, dare to P/MAU valuation, but also firmly believe that the company will generate revenue in the future VC, according to the valuation of 500 million accepted investment.
Angel wheel, the company's users, revenue, profits have nothing, P/E, P/S, P/MAU are invalid, how to value it? The company needs millions of dollars to start, because the founder is a well-known entrepreneur, so VC have invested a little more, then give 20 million, and then talk about a not too little can not too much proportion, 20%, and finally according to the valuation of 100 million transactions.
Let's summarize that the valuation method of this internet company's angel wheel is to pat the head; the valuation method of round A is P/MAU; the valuation method of round B is P/MAU, P/S; the valuation method of round C is P/MAU, P/S, P/E; and perhaps after a few years of listing, the internet company becomes a traditional company, and everyone will be valued at P/B (price-to-net ratio)! In your rethought, is it a similar situation for most financing?

For Internet companies, the P/MAU valuation system has the widest coverage and the P/E valuation system has the narrowest coverage. Here, I call this coverage system the order of the valuation system.
P/MAU is a low-order valuation system with the highest tolerance, and P/E is a high-order valuation system with the highest requirements for companies.
Different valuation methods go the same way, let's look at a formula:
Net profit - Revenue - Cost expenses . .The number of × is a single user contribution -cost charge
Net profit (E, earning), revenue (S, sales),Number of users (MAU), Single User Contribution (ARPU)
In general, if the enterprise does not have E, you can also vote S, if you do not have S, you can also invest in MAU, but ultimately expect traffic to be converted into revenue, revenue can be converted into profit. Different start-up enterprises, are at different stages, some belong to the stage of desperately expanding the number of users, some belong to the stage of racking their brains to make traffic cash, some belong to the stage of thinking every day how to achieve profitability. In the end, however, we have to look at a company by profit, when the valuation methods of different orders were the same.
Why well-developed companies will be "B-wheel dead", "C-round dead": some companies have a large user base, but always can not convert income, if in the next round (assuming it is B-round), investors are determined to according to the high-level valuation system P/S valuation, then the company's valuation is 0, not capital , so there will be B round death; some companies income scale is also good, but always do not see the hope of profit, if in the next round (assuming it is round C), facing only the net profit valuation of PE institutions, they feel that the company P/E valuation of 0, the company can not invest, there will be C round death.

In different economic cycles, the scope of use of the valuation system shifts: in a bull market, the valuation system moves back, which explains why many companies that have not made a net profit in the past two years have received round c, wheel D, or even round E, and are invested by traditional PE institutions because they have lowered their ranks and started using P/S, a low-order tool.
In a bear market, the valuation system will move forward, which can explain why since the second half of this year, some of the revenue and user number of well-developed companies are not able to invest, or even can only merge to hold the group heating, because even many VCs also require profits, we put the low-level valuation system snow hidden.
The policy of the secondary market has a clear guiding effect: Why has China been short of RMB VC?
Part of the reason is that China's public capital markets recognize only P/E as a high-level valuation system. Let's look at the GEM issuance rules: "(1) consecutively profitable for two consecutive years, cumulative net profit of not less than 10 million yuan ... Or (2) the net profit of the latest year is not less than 5 million yuan, operating income is not less than 50 million yuan ...". There must be so much profit to go public in order to have value in the secondary market, this valuation system is too demanding.
When the enterprise has only the number of users, only the size of revenue, even if your number of users is 1 billion people, your income size of 10 billion, as long as there is no profit, the valuation is all 0! So RMB VC is very few, PE a lot, because they responded to the government's call to use only the price-earnings ratio of this tool, otherwise there is no exit channel! But U.S. and Hong Kong stocks have P/S test indicators, as long as a certain scale can become a public company listing. If a company can be valued only by P/S for a considerable period of time after listing (and possibly ultimately by P/E), it will open up most of the company's stages of development and make each round of valuation smooth.
At this end, the intrinsic relationship of various valuation systems and the use of methods to explore, I hope that you entrepreneurs and investors readers can apply these principles between the bulls and bears, between rounds of financing, I hope that legislators readers can pay attention to the power of the valuation system at all levels, and actively improve the rules to play its role in guiding innovation.
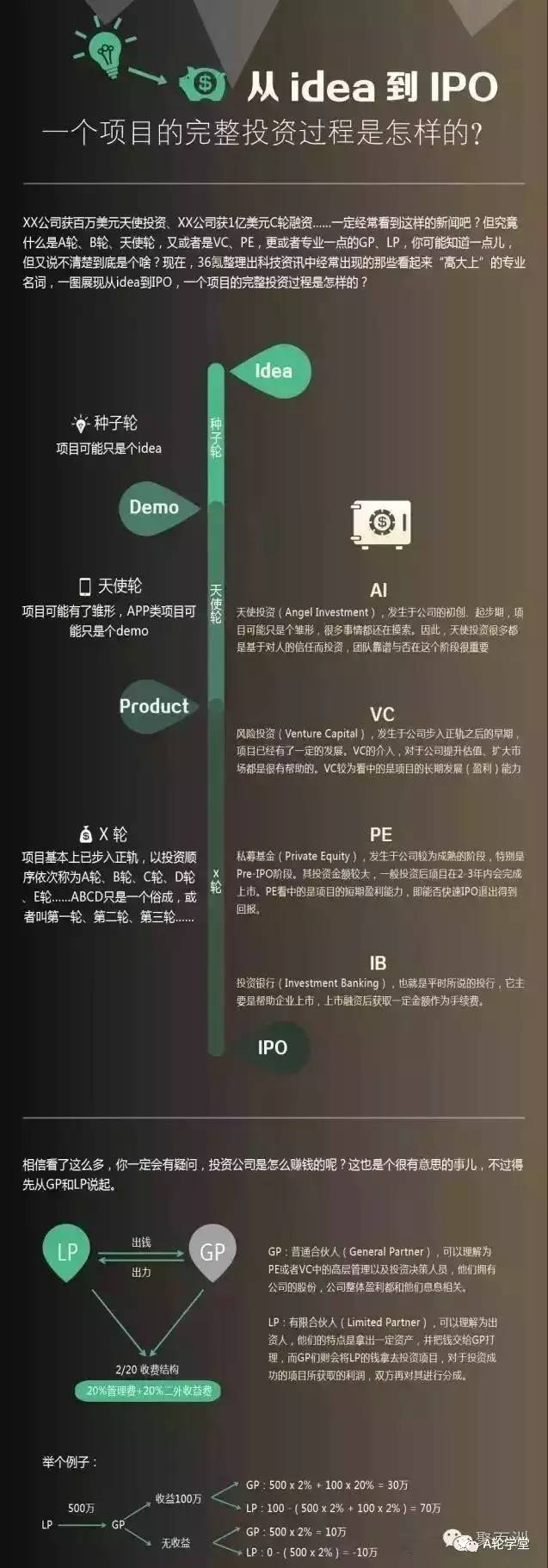
A picture to understand: A wheel, B wheel, angel wheel, VC, PE, GP, LP:
Thanks for reading, your attention is our sustained pre-action force, please sweep the QR code below to follow, orPlease find WeChat public number "Yue Dao Finance" attention, thank you!

Read good books together and accompany them all the way
Go to "Discovery" - "Take a look" browse "Friends are watching"